Body Systems and Their Functions: A Complete Guide to the Human Body
The human body is a complex and well-organized structure made up of different body systems. Each system performs specific functions that help the body survive, grow, and maintain balance. Understanding the human body systems and their functions is essential for students, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in health and wellness.
Below is a detailed explanation of the major body systems and functions, explained clearly in points.
1. Skeletal System
- The skeletal system consists of 206 bones, joints, cartilage, and ligaments.
- It provides structure and shape to the human body.
- It protects vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs.
- Bones store essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
- It helps in movement by working together with muscles.
- The bone marrow produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Main Function: Support, protection, and blood cell formation.
2. Muscular System
- The muscular system includes skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles.
- It allows the body to move and perform physical activities.
- Muscles help maintain posture and balance.
- Smooth muscles control involuntary movements such as digestion.
- Cardiac muscles help the heart pump blood throughout the body.
- Muscle contraction produces body heat, helping regulate temperature.
Main Function: Movement, posture, and heat production.
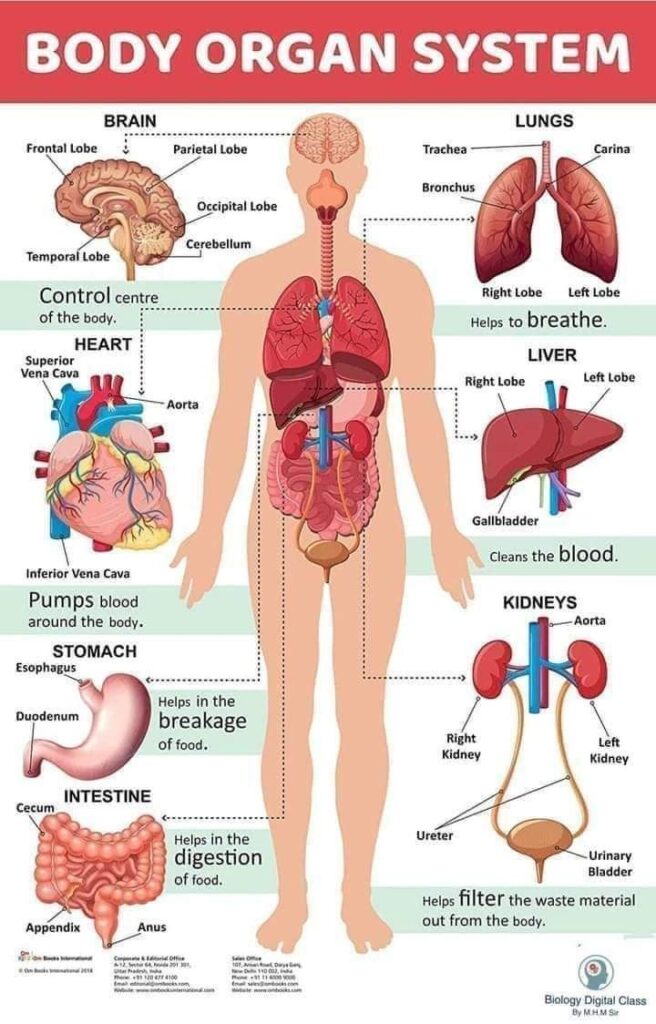
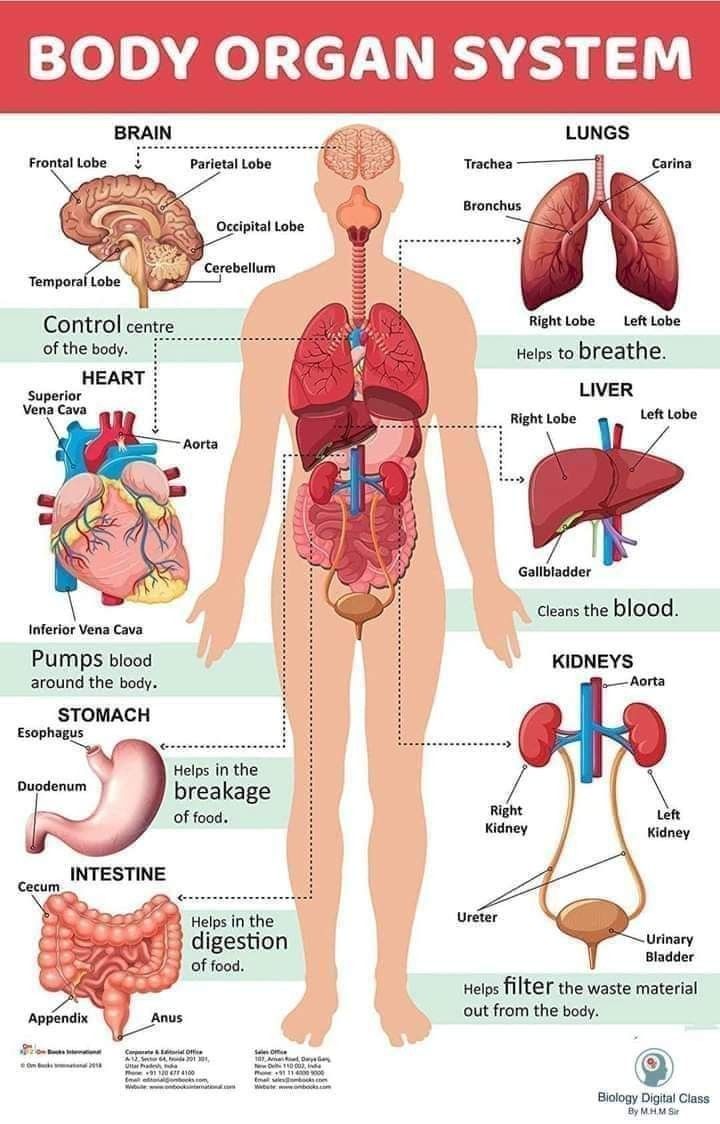
3. Nervous System
- The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- It controls both voluntary and involuntary actions.
- It helps in thinking, learning, memory, and emotions.
- Nerves transmit signals between the brain and body parts.
- It controls reflex actions like blinking and withdrawing from pain.
- It helps the body respond quickly to external stimuli.
Main Function: Control, coordination, and communication.
4. Circulatory system
- The circulatory system includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels.
- It transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and enzymes.
- It removes waste products like carbon dioxide from the body.
- Blood helps fight infections through white blood cells.
- It regulates body temperature and pH balance.
- The heart pumps blood continuously to keep organs functioning.
Main Function: Transportation of substances throughout the body.
5. Respiratory System
- The respiratory system includes the nose, trachea, lungs, and diaphragm.
- It helps in breathing and gas exchange.
- Oxygen is taken into the lungs and delivered to the blood.
- Carbon dioxide is removed from the body during exhalation.
- It supports cellular respiration, which produces energy.
- It helps maintain the body’s acid-base balance.
Main Function: Oxygen supply and carbon dioxide removal.
6. Digestive System
- The digestive system includes the mouth, stomach, liver, pancreas, and intestines.
- It breaks down food into nutrients.
- Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream for energy and growth.
- It helps in the digestion of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
- Waste materials are eliminated from the body.
- Digestive enzymes play a major role in food breakdown.
Main Function: Digestion, absorption, and waste elimination.
7. Excretory (Urinary) System
- The excretory system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- It removes toxic waste and excess water from the body.
- Kidneys filter blood to produce urine.
- It maintains fluid and electrolyte balance.
- It helps regulate blood pressure.
- It maintains overall internal balance (homeostasis).
Main Function: Waste removal and fluid balance.
8. Endocrine System
- The endocrine system consists of glands like the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
- It releases hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Hormones regulate growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
- It controls mood, stress response, and energy levels.
- It works closely with the nervous system.
- Hormonal balance is essential for overall health.
Main Function: Hormonal regulation and long-term control.
9. Reproductive System
- The reproductive system differs in males and females.
- It helps in reproduction and continuation of life.
- It produces sex cells (sperm and ova).
- It releases sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
- In females, it supports pregnancy and childbirth.
- It plays a role in sexual development.
Main Function: Reproduction and hormone production.
10. Immune System
- The immune system protects the body from infections and diseases.
- It includes white blood cells, antibodies, and lymph nodes.
- It identifies and destroys harmful microorganisms.
- It provides immunity through vaccination and natural defense.
- It helps heal injuries and fight inflammation.
- A strong immune system ensures overall health.
Main Function: Defense against diseases.
Conclusion
The human body systems and their functions work together to maintain balance and ensure survival. Each system plays a vital role, and disruption in one system can affect overall health. Understanding these body systems helps promote healthy lifestyle choices and better awareness of how the body functions.
Maintaining proper nutrition, exercise, sleep, and stress management supports all body systems and leads to a healthier life.